the developer has one app on fdroid if that means anything to you
MinekPo1 [it/she]
nya !!! :3333 gay uwu
I’m in a bad place rn so if I’m getting into an argument please tell me to disconnect for a bit as I dont deal with shit like that well :3
- 0 Posts
- 104 Comments

 2·11 days ago
2·11 days agounity kinda does this ! there is a json file wirh a base-64 encoded string (UTF-16 encoding) and is a completely different data structure with embedded json
actually they would be correct :
USB began as a protocol where one side (USB-A) takes the leading role and the other (USB-B) the following role . this was mandated by hardware with differently shaped plugs and ports . this made sense for the time as USB was ment to connect computers to peripherals .
however some devices don’t fit this binary that well : one might want to connect their phone to their computer to pull data off it , but they also might want to connect a keyboard to it , with the small form factor not allowing for both a USB-A and USB-B port. the solution was USB On-The-Go : USB Mini-A/B/AB and USB Micro-A/B/AB connectors have an additional pin which allows both modes of operations
with USB-C , aside from adding more pins and making the connector rotationally symmetric , a very similar yet differently named feature was included , since USB-C - USB-C connections were planed for
so yeah USB-A to USB-A connections are explicitly not allowed , for a similar reason as you only see CEE 7 (fine , or the objectively worse NEMA) plugs on both ends of a cable only in joke made cables . USB-C has additional hardware to support both sides using USB-C which USB-A , neither in the original or 3.0 revision , has .
yeah thats the point , the cybertruck design is retrofuturism

 2·5 months ago
2·5 months agoAgh I made a mistake in my code:
if (recalc || numbers[i] != (hashstate[i] & 0xffffffff)) { hashstate[i] = hasher.hash(((uint64_t)p << 32) | numbers[i]); }Since I decided to pack the hashes and previous number values into a single array and then forgot to actually properly format the values, the hash counts generated by my code were nonsense. Not sure why I did that honestly.
Also, my data analysis was trash, since even with the correct data, which as you noted is in a lineal correlation with n!, my reasoning suggests that its growing faster than it is.
Here is a plot of the incorrect ratios compared to the correct ones, which is the proper analysis and also clearly shows something is wrong.
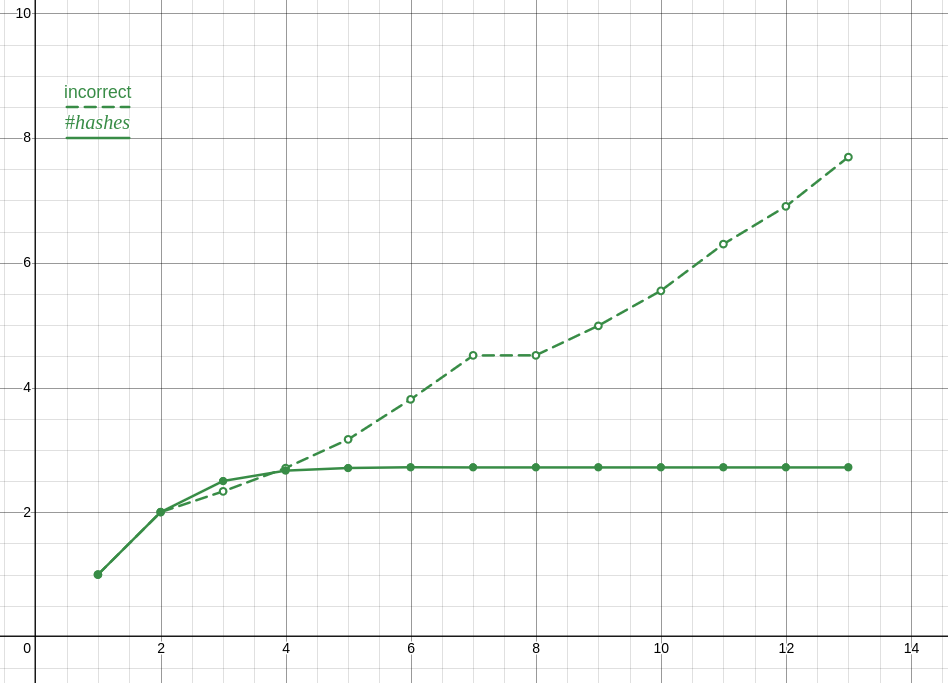
Anyway, and this is totally unrelated to me losing an internet argument and not coping well with that, I optimized my solution a lot and turns out its actually faster to only preform the check you are doing once or twice and narrow it down from there. The checks I’m doing are for the last two elements and the midpoint (though I tried moving that about with seemingly no effect ???) with the end check going to a branch without a loop. I’m not exactly sure why, despite the hour or two I spent profiling, though my guess is that it has something to do with caching?
Also FYI I compared performance with
-O3and after modifying your implementation to use sdbm and to actually use the previous hash instead of the previous value (plus misc changes, see patch).

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agoyou forgot about updating the hashes of items after items which were modified , so while it could be slightly faster than O((n!×n)²) , not by much as my data shows .
in other words , every time you update the first hash you also need to update all the hashes after it , etcetera
so the complexity is O(n×n + n×(n-1)×(n-1)+…+n!×1) , though I dont know how to simplify that

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agoactually all of my effort was wasted since calculating the hamming distance between two lists of n hashes has a complexity of O(n) not O(1) agh
I realized this right after walking away from my devices from this to eat something :(
edit : you can calculate the hamming distance one element at a time just after rehashing that element so nevermind

 2·5 months ago
2·5 months agohonestly I was very suspicious that you could get away with only calling the hash function once per permutation , but I couldn’t think how to prove one way or another.
so I implemented it, first in python for prototyping then in c++ for longer runs… well only half of it, ie iterating over permutations and computing the hash, but not doing anything with it. unfortunately my implementation is O(n²) anyway, unsure if there is a way to optimize it, whatever. code
as of writing I have results for lists of n ∈ 1 … 13 (13 took 18 minutes, 12 took about 1 minute, cant be bothered to run it for longer) and the number of hashes does not follow n! as your reasoning suggests, but closer to n! ⋅ n.
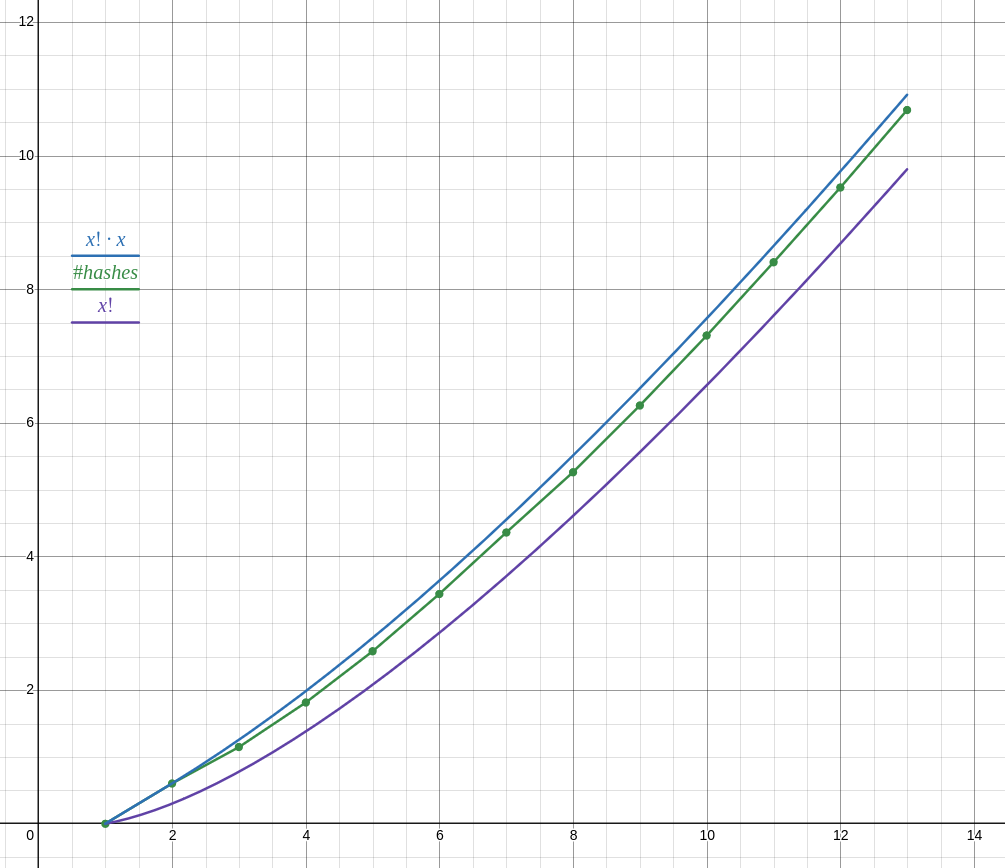
anyway with your proposed function it doesn’t seem to be possible to achieve O(n!²) complexity
also dont be so negative about your own creation. you could write an entire paper about this problem imho and have a problem with your name on it. though I would rather not have to title a paper “complexity of the magic lobster party problem” so yeah

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agounless the problem space includes all possible functions f , function f must itself have a complexity of at least n to use every number from both lists , else we can ignore some elements of either of the lists , therby lowering the complexity below O(n!²)
if the problem space does include all possible functions f , I feel like it will still be faster complexity wise to find what elements the function is dependant on than to assume it depends on every element , therefore either the problem cannot be solved in O(n!²) or it can be solved quicker

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agothis would assume that finding the next prime is a linear operation , which is false

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agoif I’m not mistaken , a example of a problem where O(n!²) is the optimal complexity is :
There are n traveling salespeople and n towns . find the path for each salesperson with each salesperson starting out in a unique town , such that the sum d₁ + 2 d₂ + … + n dₙ is minimised, where n is a positive natural number , dᵢ is the distance traveled by salesperson i and i is any natural number in the range 1 to n inclusive .
pre post edit, I realized you can implement a solution in 2(n!) :(

 3·5 months ago
3·5 months agoMozilla has a history of harming me. I’ve documented this as one more case of attacks from Mozilla to go along with everything else. I see no reason to put up with it or tolerate it. Mozilla should expect that one day they’re going to be held accountable. If people at Mozilla aren’t aware of the unethical behavior it regularly engages in including an exploitative approach to contributors, they should inform themselves.
- Daniel Micay (im the linked mailing list thread)
it doesn’t seem like Micay had feuds previous to 2019 with Mozilla , though I was unable to find what he is referring to unfortunately .

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agoalso I would recommend this video & and others by shounic
I misread this as if it lacked the y and was slightly confused for a second

 1·6 months ago
1·6 months agoto be fair , neither the free software movement nor the open source movement (which are distinct ideologically) are explicitly socialist . in a way , especially the free software movement , they embody an extention of liberalism .
both of these movements focus on the individuals freedom and take issue not with developers/companies being systemically incentivized to develop closed source / nonfree software , but with individual developers/companies doing so . thus the solution taken is limited to the individual not to systemic change .
LMMS isn’t really a DAW, as it can’t really manipulate audio easily, only midi.
IIRC it can use audio files as instruments though I never used that feature so idk how limited it is , I believe other DAWs can import audio more directly

 21·7 months ago
21·7 months agoautistic complaining about units
ok so like I don’t know if I’ve ever seen a more confusing use of units . at least you haven’t used the p infix instead of the / in bandwith units .
like you used both upper case and lowercase in units but like I can’t say if it was intentional or not ? especially as the letter that is uppercased should be uppercased ?
anyway
1Mb
is theoretically correct but you likely ment either one megabyte (1 MB) or one megibyte (MiB) rather than one megabit (1 Mb)
~325mb/s
95mb/s
and
9mb/s
I will presume you did not intend to write ~325 milibits per second , but ~325 megabits per seconds , though if you have used the 333 333 request count as in the segment you quoted , though to be fair op also made a mistake I think , the number they gave should be 3 exabits per second (3 Eb/s) or 380 terabytes per seconds (TB/s) , but that’s because they calculated the number of requests you can make from a 1 gigabit (which is what I assume they ment by gbit) wrong , forgetting to account that a byte is 8 bits , you can only make 416 666 of 4 kB (sorry I’m not checking what would happen if they ment kibibytes sorry I underestimated how demanding this would be but I’m to deep in it now so I’m gonna take that cop-out) requests a second , giving 380 terabits per second (380 Tb/s) or 3.04 terabytes per second (3.04 TB/s) , assuming the entire packet is exactly 114 megabytes (114 MB) which is about 108.7 megibytes (108.7 MiB) . so anyway
packet size theoretical bandwidth 1 Mb 416.7 Gb/s 52.1 GB/s 1 MB 3.3 Tb/s 416.7 GB/s 1 MiB 3.3 Tb/s 416.7 GB/s 300 kb 125.0 Gb/s 15.6 GB/s 300 kB 1000.0 Gb/s 125.0 GB/s 300 kiB 1000.0 Gb/s 125.0 GB/s 30 kb 12.5 Gb/s 1.6 GB/s 30 kB 100.0 Gb/s 12.5 GB/s 30 kiB 100.0 Gb/s 12.5 GB/s hope that table is ok and all cause im in a rush yeah bye

 1·7 months ago
1·7 months agoI once deleted
/usr/binwhile trying to delete/bin(symbolic link) because I accidentally misformed it . don’t remember why I had to recreate/binin the first place but it had something to do with installing java


the frames definetly can impact how thick the lenses look . my previous glasses looked quite thick but despite my prescription being higher the new ones look not as thick